Crypto CSV to Excel
Crypto CSV to Excel refers to the process of importing, normalizing, and reconciling cryptocurrency transaction data exported as CSV files from exchanges, wallets, and custodians, and making that data usable inside Excel.
In the crypto domain, CSV files are the primary way historical data is provided. However, Excel becomes reliable only after this data has been transformed into a coherent and standardized structure.
Why crypto CSV files are inconsistent
There is no shared standard for crypto CSV exports.
CSV files differ across providers in:
column names and ordering
transaction type vocabularies
asset and symbol naming
fee representation
timestamp formats and timezones
separation of trades, deposits, withdrawals, rewards, and other operations
As a result, CSVs from different sources may describe the same economic event using incompatible structures and meanings.
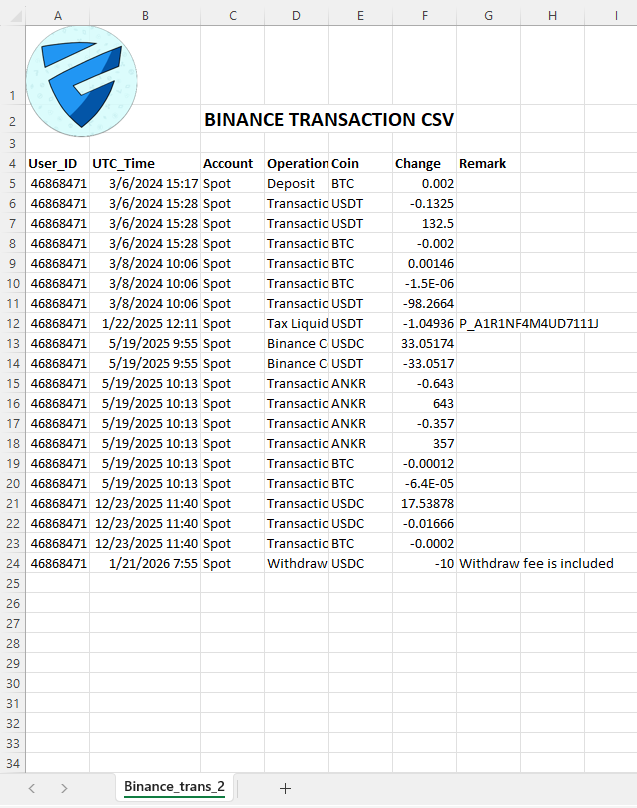
The normalization problem
Before crypto data can be used in Excel, it must be normalized.
Normalization includes:
cleaning and validating column headers
standardizing transaction types
normalizing asset symbols
converting timestamps to a consistent time basis
enforcing coherent quantity and fee semantics
removing structural ambiguities
Without normalization, Excel calculations and summaries are unreliable.
Multi-exchange and multi-wallet reconciliation
Most users operate across multiple exchanges and wallets.
This introduces additional complexity:
transfers appearing as withdrawals on one platform and deposits on another
duplicated or fragmented records
different fee accounting models
misaligned historical time ranges
Reconciliation is the process of identifying and aligning related records so that Excel reflects the underlying activity rather than a simple aggregation of CSV files.
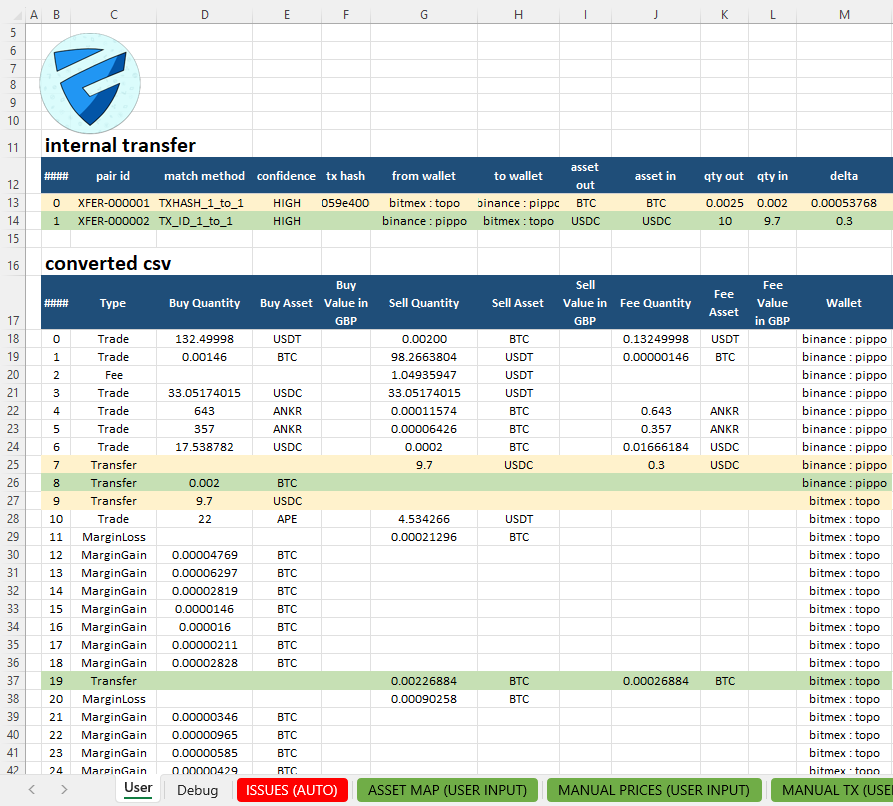
Excel as the canonical data layer
Excel can function correctly only when it is fed with a canonical dataset.
A canonical Excel data layer means:
one row represents one economic event
each column has a fixed and unambiguous meaning
data is deterministic and auditable
all downstream logic starts from the same base
This turns Excel into a structured data reference, not just a collection of tables.
When data are structured we can perform a portfolio analysis and calculate crypto taxes
Excel as an interactive front end
In this architecture, Excel primarily acts as an interactive front end.
Excel is where users:
inspect and validate normalized data
filter, sort, and explore transactions
review reconciliation outcomes
intervene manually when data interpretation is ambiguous
All data ingestion, normalization, and reconciliation logic is executed in Python, outside of Excel.
Python is responsible for:
CSV parsing and validation
exchange- and wallet-specific normalization
deterministic reconciliation rules
construction of the canonical dataset consumed by Excel
Excel exposes the final result and remains fully interactive, while the underlying logic stays reproducible, auditable, and independent from spreadsheet formulas.
For those interested in understanding all the benefits of using Excel for crypto data analysis, CryptoExcel also provides a dedicated guide on the advantages of an Excel add-in for digital assets.
What good crypto data looks like in Excel
Well-prepared crypto data in Excel is:
exchange-agnostic
wallet-aware
chronologically consistent
free from semantic duplication
suitable for filtering, pivoting, auditing, and verification
Only at this stage can Excel be used reliably.
Typical use cases
preparing data for portfolio analysis
preparing data for tax calculations
reconciling historical activity across platforms
auditing transactions and balances
building custom Excel models on crypto data
Scope and internal links
This page covers crypto CSV ingestion, normalization, and reconciliation only.
For downstream applications:
FAQs
Are exchange CSV files already ready for Excel?
No.
Exchange CSV files are designed for data export, not for structured analysis in Excel. Column layouts, timestamp formats, transaction types, and fee handling vary widely. Without normalization, Excel processes structurally inconsistent data.
Why is reconciliation across multiple CSV files necessary?
Because the same operation can appear in multiple files with different meanings.
A transfer, for example, may show as a withdrawal on one platform and a deposit on another. Reconciliation aligns these records so Excel reflects the underlying activity correctly.
Does Excel perform the data normalization logic?
No.
Excel acts as an interactive front end.
CSV ingestion, normalization, and reconciliation logic is executed in Python. Excel exposes the resulting canonical dataset and allows users to analyze, verify, and interact with it.
